In the world of network routing, Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) stands as a cornerstone. Among its many facets, the concept of the BGP default route is particularly significant.
This article aims to provide a comprehensive exploration of all configuration options related to BGP default routes. Also, providing practical examples in a LAB.
BGP Default Route Overview
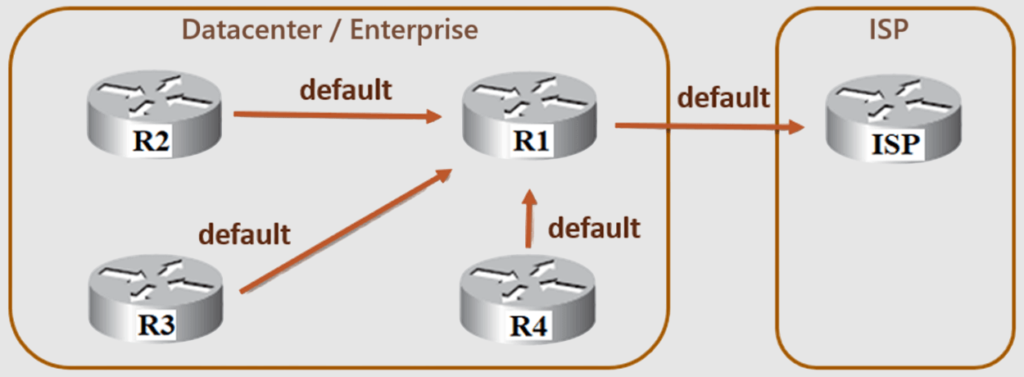
Datacenters typically use default routes in two different cases:
- Direct the remote-site routers at the edge of the data center network in order to send all packets toward the data center’s core, with the core routers knowing more specific routes.
- Direct traffic on all data center routers toward the Internet-facing router to reach Internet destinations.
In Cisco NX-OS, we can inject the default route into BGP using one of the following:
- The network 0.0.0.0/0 command.
- The redistribute with default-information originate commands.
- The neighbor’s default-originate command.
BGP Default Route Using The ‘Network’ Command
When injecting a default route into the BGP table using the network 0.0.0.0/0 command, a default route (0.0.0.0/0) should exist in the local routing table (RIB).
The default route can be learned through any means, but if it’s removed from the routing table, BGP withdraws it from the BGP table (RIB). We can populate the routing table with a static default route pointing to null 0.
BGP Default Route Using The ‘Redistribute‘ Command
Injecting a default route through the redistribute command requires the default-information originate address-family BGP command.
The default route must first exist in the routing table (RIB) using either IGP or static routing. Then, you can use a static default route to null0. After that, use the redistribute static route-map command to redistribute the static default route.
BGP Default Route Using the ‘Neighbor Default-Originate’ Command
Using this method, the BGP router doesn’t add the default route into the local BGP table; instead, it causes the advertisement to the specified neighbor (BGP peer).
neighbor a.b.c.d
address-family ipv4 unicast
default-originate [route-map route-map-name]By default, this method doesn’t check if the default route exists in the routing table.
The referenced route map examines the entries in the IP routing table (not the BGP table). Therefore, if a route map permit clause is matched, the default route is advertised to the neighbor. So, the route map can be used to track the default route or any other route in the local routing table to be used as a condition for the advertisement.
BGP Default Route LAB Demo in Cisco NX-OS
The video below demonstrates the three BGP default route configuration methods in Cisco Nexus switches:
Summary
In conclusion, we can inject the default route into BGP using one of the following:
- The
network 0.0.0.0/0command. - The
redistributewithdefault-information originatecommands. - The neighbor’s
default-originatecommand. - The BGP path attributes determine which default route (or any route) the BGP router should consider when receiving a BGP update.
References:
Configure BGP to Advertise a Default Route on Nexus Switches
Cisco NX-OS vs. IOS: Your Guide to BGP Route Redistribution
Looking for Comprehensive Cisco Data Center Training?
Take your data center skills to the next level with my deep-dive courses, designed for real-world application.
Modern DC Architecture & Automation (Self-paced Courses):
- Cisco Data Centers | ACI Core
- Cisco Data Centers | ACI Automation With Ansible
- Cisco Data Centers | VXLAN EVPN
Core Protocols & CCIE Prep (Self-paced Courses):
Live Intensive Training (Cohort):
Need Personalized Guidance (1:1 Mentorship)?


I appreciate the effort that goes into creating high-quality content, and this post was no exception. The insights and information were top-notch and made for a really engaging read. Keep up the great work!
Thank you so much for taking the time to share your feedback. Your support means a lot and helps fuel the next set of labs and posts.